Research Status and Hotspot Analysis of Dangerous Goods Transportation by Waterway in China
-
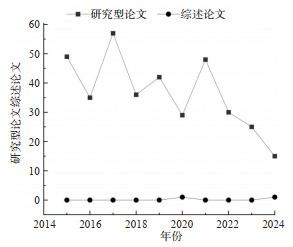
摘要: 随着全球经济的持续扩张和工业水平的持续提升,各国对能源和化工产品的需求不断攀升,而此类化工产品多属于危险品。由于具备运输成本低、运量大、安全、环保及运输范围广等优势,水路运输已经成为危险品运输的主要方式。近年来,为提升水路危险品运输的安全和效率,国内学者开展了大量研究。为系统梳理国内在该领域的研究现状与未来发展趋势,本文检索了2015—2024年发表在中文核心期刊上的相关文献,共计368篇。通过对检索文献的年度发文量、期刊分布、研究机构及代表性学者进行统计分析,并利用VOSviewer软件对关键词进行聚类和演化趋势分析,本文将研究热点归纳为危险品船舶设计、危险货物运输管理、运输风险评估及应急处置这4个主要方面。当前研究在船舶设计的创新性、运输管理的智能化、风险评估的精准化以及应急处置的高效化方面取得了一定进展,但仍面临设计与安全管理智能化程度不高、风险评估全面性不足、应急处置设备针对性不强等问题。未来研究应聚焦于人工智能技术在危险品船设计与营运安全状态监控中的应用,以及推动绿色低碳技术在船舶能效优化、动力替代方面的集成,以提升水路危险品运输的安全性与可持续性。Abstract: With the continuous expansion of the global economy and the sustained improvement of the industrial level, the demand for energy and chemical products is constantly increasing in various countries, and such chemical products are mostly classified as dangerous goods. Due to its advantages of low transportation cost, large capacity, safety, environmental friendliness, and wide transport range, waterway transportation has become the primary mode for the transport of dangerous goods. In recent years, to enhance the safety and efficiency of waterway transportation of dangerous goods, domestic scholars have conducted a large amount of research. To systematically review the current research status and future development trends in this field in China, this paper retrieved 368 relevant docu-ments published in Chinese core journals from 2015 to 2024. Through statistical analysis of the annual publication volume, journal distribution, research institutions, and key scholars of the retrieved literature, and using VOSviewer software for keyword clustering and evolutionary trend analysis, this paper summarizes the research hotspots into four main aspects: design of dangerous goods ships, management of dangerous goods transportation, transportation risk assessment, and emergency response. Current research has made certain progress in the innovation of ship design, intelligent management of transportation, precise risk assessment, and efficient emergency response, but it still faces challenges such as low intelligence in design and safety management, insufficient comprehensiveness in risk assessment, and lack of targeted emergency response equipment. Future research should focus on the application of artificial intelligence technology in the design and operational safety monitoring of hazardous material ships, as well as promoting the integration of green and low-carbon technologies in ship energy efficiency optimization and power sub-situation, to enhance the safety and sustainability of waterway transportation of dangerous goods.
-
表 1 水路危险品运输主要期刊发文量分布
Table 1. Distribution of publication volume in major journals of dangerous goods waterway transportation
序号 期刊 发文量 1 《航海工程》 83 2 《船舶工程》 69 3 《船舰科学与技术》 41 4 《中国航海》 2 5 《水运工程》 20 6 《中国造船》 20 7 《上海海事大学学报》 9 8 《船舶力学》 8 9 《上海船舶运输科学研究所学报》 7 10 《安全与环境学报》 6 11 《大连海事大学学报》 6 12 《化工学报》 5 13 《油气储运》 5 14 《中国舰船研究》 5 合计 309 表 2 水路危险品运输主要研究机构和代表性学者
Table 2. Main research institutions and representative scholars in the transportation of dangerous goods by waterway
机构 发文量/篇 代表性学者 研究方向 上海交通大学 36 唐文勇 LNG船结构可靠性分析 中国船舶及海洋工程设计研究院 28 郑文青 LNG船货舱结构研究 中海油能源发展股份有限公司 25 周毅 LNG船舶设计 大连海事大学 23 吴宛青 油船/LNG船风险分析 武汉理工大学 23 朱汉华 油气储运技术与安全工程 上海外高桥造船有限公司 22 甘水来 油船防溢设计 上海海事大学 15 席永涛 危险品船风险分析 沪东中华造船(集团)有限公司 13 刘金峰 LNG船货舱设计 江苏科技大学 13 姚寿广 LNG动力船设计 浙江海洋大学 13 吴文锋 油船碰撞风险分析 中国船舶科学研究中心 11 程成 LNG船强度分析 -
[1] 恒州博智国际信息咨询有限公司. 2024—2030全球及中国危险品运输行业研究及十五五规划分析报告[R]. 北京: 恒州博智国际信息咨询有限公司, 2024.QY Research. 2024—2030 global and China transportation of dangerous goods(TDG)industry research and 15th five year plan analysis report[R]. Beijing: QY Research, 2024. (in Chinese) [2] 严新平, 韩亚, 吴兵, 等. 水路交通系统的发展现状与未来展望[J]. 中国航海, 2024, 47(2): 145-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2024.02.019YAN X P, HAN Y, WU B, et al. Current development and future prospects of waterborne transportation system[J]. Navigation of China, 2024, 47(2): 145-152. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2024.02.019 [3] 郑云亮, 赵杰超, 王吉武, 等. 水上危化品运输事故分析及应急处置能力提升研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2023, 45(9): 69-74. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2023.09.015ZHENG Y L, ZHAO J C, WANG J W, et al. Analysis of maritime transport accidents of hazardous chemicals and research on the improvement of emergency response capabilities[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2023, 45(9): 69-74. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2023.09.015 [4] KIM S J, LEE S J, LEE H Y, et al. Development of unmanned air and water vehicle disaster-management payload and monitoring systems for marine chemical accident response[J]. Journal of Environmental Analysis, Health and Toxicology, 2020, 23(1): 37-46. doi: 10.36278/jeaht.23.1.37 [5] 吴建华, 彭虎, 王辰, 等. 基于AIS通信量的水上交通事故检测方法[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2023, 41(5): 83-94. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2023.05.009WU J H, PENG H, WANG C, et al. A detection method for maritime traffic accidents based on AIS communication volume[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2023, 41(5): 83-94. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2023.05.009 [6] 孙权, 吴赞, 黄国富, 等. 满足第Ⅲ阶段EEDI指标的3万吨化学品绿色船型开发[J]. 中国造船, 2018, 59(2): 42-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.02.005SUN Q, WU Z, HUANG G F, et al. Development of 30 000 ton chemical green ship type meeting EEDI index in phase Ⅲ[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2018, 59(2): 42-50. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2018.02.005 [7] 彭贵胜, 高阳, 王文华, 等. Aframax油船自航性能的数值和试验研究[J]. 船舶力学, 2020, 24(6): 754-763. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2020.06.006PENG G S, GAO Y, WANG W H, et al. Numerical and experimental study on self-propulsion performance of Aframax tanker[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics. 2020, 24(6): 754-763. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2020.06.006 [8] 刘英良, 蒋武杰, 刘嵩. 基于CFD的超大型液化气船型线优化[J]. 船海工程, 2018, 47(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2018.01.001LIU Y L, JIANG W J, LIU S. Optimization of super large liquefied gas ship based on CFD[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2018, 47(1): 1-5. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2018.01.001 [9] 冯国庆, 常琦, 王元, 等. 复杂约束条件下大型油船中剖面结构优化[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47 (10): 75-81.FENG G Q, CHANG Q, WANG Y, et al. Mid-section structure optimization for large oil tankers under complex constraints[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 75-81. (in Chinese) [10] 丁悦, 郭世玺. 极地破冰型阿芙拉油船的线型设计[J]. 船海工程, 2019, 48(2): 122-126. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2019.02.032DING Y, GUO S X. Linear design of polar ice breaking Aframax[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2019, 48(2): 122-126. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2019.02.032 [11] 杨朕, 张利军, 曹凯, 等. 穿梭油船波浪载荷直接计算分析[J]. 中国航海, 2019, 42(1): 34-37, 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.01.007YANG Z, ZHANG L J, CAO K, et al. Direct calculation and analysis of wave load on shuttle tanker[J]. Navigation of China, 2019, 42(1): 34-37, 46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4653.2019.01.007 [12] 杨鹏, 顾学康, 丁军, 等. 大型油船和散货船波激振动及其对结构疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 船舶力学, 2016, 20(10): 1320-1329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2016.10.012YANG P, GU X K, DING J, et al. Study on springing of large oil tanker and bulk carrier and the influence to fatigue[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2016, 20 (10): 1320-1329. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2016.10.012 [13] 王元, 王德禹. 考虑晃荡效应的独立B型LNG液舱结构多目标优化[J]. 海洋工程, 2016, 34(2): 88-94.WANG Y, WANG D Y. Structural multi-objective optimization of SPB LNG tanks under sloshing pressure[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2016, 34(2): 88-94. (in Chinese) [14] 张吉萍, 邵珠峰, 杨阳, 等. 考虑液货晃荡的油船运动与结构响应研究[J]. 中国造船, 2017, 58(4): 83-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2017.04.010ZHANG J P, SAO Z F, YANG Y, et al. Research on motion and structural response of oil tanker considering sloshing of liquid cargo[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2017, 58(4): 83-90. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2017.04.010 [15] 唐亮, 李玉星, 臧垒垒, 等. 不同LNG液舱对晃荡敏感性的数值模拟[J]. 油气储运, 2017, 36(7): 849-854, 860.TANG L, LI Y X, ZANG L L, et al. Numerical simulation on the sensitivity of LNG liquid tank to sloshing[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2017, 36(7): 849-854, 860. (in Chinese) [16] 张明娟, 刘俊, 薛鸿祥, 等. 独立B型LNG船液舱晃荡强度分析方法[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2017, 39(17): 59-63, 73.ZHANG M J, LIU J, XUE H X, et al. Strength analysis measures of LNG ship with independent type B tanks under sloshing load[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2017, 39(17): 59-63, 73. (in Chinese) [17] 焦玲玲, 赵路, 杨会, 等. 晃荡对CSR油船设计的影响[J]. 船海工程, 2021, 50(2): 91-93, 97.JIAO L L, ZHAO L, YANG H, et al. Influence of sloshing on CSR tanker design[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2021, 50(2): 91-93, 97. (in Chinese) [18] ZHAO M M, JIAO J L. Smoothed-Particle Hydrodynamics simulation of ship motion and tank sloshing under the effect of regular waves[J]. Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, 2024, 20(5): 1045-1061. [19] 官文锋, 田宇忠, 徐建勇. 内河船舶载运散装植物油液货舱位置分析[J]. 船海工程, 2017, 46(4): 82-85.GUAN W F, TIAN Y Z, XU J Y. Analysis on the position of the cargo tank of inland river ships carrying bulk vegetable oil[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2017, 46(4): 82-85. (in Chinese) [20] 荆明阳, 张佳宁, 张雷, 等. 基于风险最小化思想的油船分舱设计研究[J]. 中国造船, 2016, 57(1): 186-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2016.01.020JING M Y, ZHANG J N, ZHANG L, et al. Research on subdivision design of oil tanker based on risk minimization[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2016, 57(1): 186-192. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2016.01.020 [21] 王高阳, 夏利娟. 基于组合算法的VLCC货舱区综合分舱优化[J]. 中国造船, 2020, 61(4): 198-208.WANG G Y, XIA L J. Integrated subdivision optimization of VLCC cargo area based on combinatorial algorithm[J]. Shipbuilding of China, 2020, 61(4): 198-208. (in Chinese) [22] 姚志义, 郑坤, 时光志, 等. 中小型LNG船C型舱的多目标优化设计方法[J]. 船海工程, 2021, 50(3): 45-48.YAO Z Y, ZHENG K, SHI G Z, et al. Multi-objective optimization design for independent type C cargo tanks of small and medium-scaled LNG carriers[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2021, 50(3): 45-48. (in Chinese) [23] 苏绍娟, 王国回, 张祥. V型无压载水油船货舱中横剖面拓扑优化[J]. 船舶工程, 2022, 44(4): 58-63.SU S J, WANG G H, ZHANG X. Topology optimization of midship section of cargo hold of V-type non-ballast water tanker[J]. Ship Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 58-63. (in Chinese) [24] 季东. 大型油船货舱惰气及透气系统布置优化[J]. 船海工程, 2019, 48(2): 97-100.JI D. Layout optimization of inert gas and ventilation system in cargo hold of large oil tanker[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2019, 48(2): 97-100. (in Chinese) [25] 刘明, 尹其峰, 熊振东, 等. 液化气船液货区域通风设计[J]. 船海工程, 2022, 51(1): 115-119.LIU M, YIN Q F, XIONG Z D, et al. Ventilation design of liquefied gas tanker cargo area[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2022, 51(1): 115-119. (in Chinese) [26] 刘东进, 甘少炜, 顾华, 等. LNG SPB型独立液货舱设计分析[J]. 船海工程, 2017, 46(4): 102-105.LIU D J, GAN S W, GU H, et al. Design analysis of LNG SPB independent cargo tank[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2017, 46(4): 102-105. (in Chinese) [27] 章瑶, 郑雷, 刘正浩, 等. 基于回归算法的MARK Ⅲ薄膜型LNG运输船结构分析优化[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2024, 46 (8): 37-41.ZHANG Y, ZHENG L, LIU Z H, et al. Structural analysis and optimization of MARK Ⅲ membrane LNG carrier based on regression algorithm[J]. Ship Science and Technology. 2024, 46(8): 37-41. (in Chinese) [28] 吕植勇, 赵裕, 易俊威, 等. 基于系统动力学的内河危化品运输系统安全管理研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(5): 2114-2120.LYU Z Y, ZHAO Y, YI J W, et al. Transportation of dangerous chemicals in inland rivers based on system dynamics research on system security management[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(5): 2114-2120. (in Chinese) [29] 刘清, 杨锬, 杨柳, 等. 内河危化品运输从业人员安全行为能力影响机理[J]. 中国航海, 2021, 44(3): 7-12, 19.LIU Q, YANG T, YANG L, et al. Influencing factors of safety behavior capacity of workers in inland hazardous chemicals transport industry[J]. Navigation of China, 2021, 44(3): 7-12, 19. (in Chinese) [30] 郝勇, 时间, 吴昊旻. 基于冰山模型的长江危险品船船员素质评价指标体系构建[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(4): 1376-1383.HAO Y, SHI J, WU H M. Construction of quality evaluation index system for the crew of dangerous goods ship in the Yangtze River Based on iceberg model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20(4): 1376-1383. (in Chinese) [31] 刘文宝. 智能化船舶航行安全风险预警与防控在油轮安全管理中的应用[J]. 中国船检, 2023, 25(11): 19-23.LIU W B. Application of intelligent ship navigation safety risk early warning and prevention in Tanker Safety Management[J]. China Ship Survey, 2023, 25(11): 19-23. (in Chinese) [32] 薄文彦, 赵磊, 曲霄红. 无线射频技术在船舶危险品运输管理中的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2023, 45(18): 186-189.BO W Y, ZHAO L, QU X H. Application of radio frequency technology in ship dangerous goods transportation management[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2023, 45(18): 186-189. (in Chinese) [33] 许环运, 黄志勇, 武江涛, 等. 基于VLCC的液货智能管理系统设计技术[J]. 船舶工程, 2020, 42(3): 19-22.XU H Y, HUANG Z Y, WU J T, et al. Design technology of liquid cargo intelligent management system based on VLCC[J]. Ship Engineering, 2020, 42(3): 19-22. (in Chinese) [34] 刘明明, 胡甚平, 郭云龙, 等. 集装箱化危险品船载运输风险因子辨识[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(10): 168-174.LIU M M, HU S P, GUO Y L, et al. Risk factors identification of containerization dangerous goods on board[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(10): 168-174. (in Chinese) [35] 张帆, 周涂强. 基于FSA的LNG燃料动力船过闸安全性[J]. 中国航海, 2016, 39(2): 82-86.ZHANG F, ZHOU T Q, Safety assessment of LNG fuel ship passing through Three Gorges Dam lock[J]. Navigation of China, 2016, 39(2): 82-86. (in Chinese) [36] 李清, 甘少炜. 内河LNG燃料动力船通过船闸的风险评估方法[J]. 船海工程, 2016, 45(3): 6-11.LI Q, GAN S W. Risk assessment method of inland LNG fuel powered ship passing through lock[J]. Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2016, 45(3): 6-11. (in Chinese) [37] 朱清华, 胡甚平, 田力, 等. 基于二维灰云模型的LNG动力船航行过程风险推理[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(6): 180-186.ZHU Q H, HU S P, TIAN L, et al. Risk reasoning on navigation process of LNG-fueled ship based on two-dimensional gray cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(6): 180-186. (in Chinese) [38] 郑庆功, 吴宛青, 宋明. 内河LNG动力船机舱NG泄漏爆炸对人员的损伤后果[J]. 中国航海, 2019, 42(4): 51-58.ZHENG Q G, WU Y Q, SONG M. Possible casualties of NG explosion in engine room on LNG fueled inland river ship[J]. Navigation of China, 2019, 42(4): 51-58. (in Chinese) [39] 邓健, 张育铭, 史洪宾, 等. 内河LNG燃料动力船隧洞通航燃料泄漏风险评估研究[J]. 中国航海, 2021, 44(2): 108-113, 133.DENG J, ZHANG Y M, SHI H B, et al. Assessment of risks associated with fuel leakage of LNG powered inland ships in tunnel[J]. Navigation of China, 2021, 44(2): 108-113, 133. (in Chinese) [40] 韩晨健, 周春奇, 李攀, 等. 化学品船液货舱泄爆参数分析及优化评估[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2023, 45(8): 10-14.HAN C J, ZHOU C Q, LI P, et al. Parameter analyzing and optimizing of chemical tanker cargo hold explosion[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2023, 45(8): 10-14. (in Chinese) [41] 席永涛, 贾哲, 付姗姗, 等. STAMP框架下化学品船智能液货系统风险分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2023, 23(4): 1005-1013.XI Y T, JIA Z, FU S S, et al. Risk analysis of the intelligent liquid cargo system of the chemical tanker under the STAMP framework[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2023, 23(4): 1005-1013. (in Chinese) [42] 文元桥, 宋荣鑫, 张帆, 等. 长江干线船舶事故性溢油应急处置模式与应急站点选址研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版), 2021, 45(1): 18-22, 27.WEN Y Q, SONG R X, ZHANG F, et al. Study on emergence disposal mode and site selection of accident oil spill from ships in Yangtze river trunk line[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 2021, 45(1): 18-22, 27. (in Chinese) [43] LIU X J, WANG Q, ZHANG A L, et al. Ship dispatching scheme of marine oil spill emergency material based on genetic algorithm[C]. 6th International Conference on Transportation Engineering, Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2019. [44] YI A N, ZHANG H M. Oil spill collection boom of ship based on negative pressure principle[C]. 5th International Conference on Advances in Energy Resources and Environment Engineering, Chongqing, China: Yantai University, 2019. [45] 李尚宇, 邓健, 马泽泰, 等. 面向内河船舶污染应急的溢油浮标系统[J]. 船舶工程, 2021, 43(7): 102-106.LI S Y, DENG J, MA Z T, et al. Oil spill buoy system for pollution emergency of inland ships[J]. Ship Engineering, 2021, 43(7): 102-106. (in Chinese) [46] 甘水来, 蒋伟. 超大型油船溢油防护结构设计研究[J]. 船舶工程, 2016, 38(3): 5-9.GAN S L, JIANG W. Design Study of spill coaming on very large crude carrier[J]. Ship Engineering, 2016, 38(3): 5-9. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: