A Vehicle Re-identification Method Based on Feature Interaction and Multi-modal Adaptive Fusion
-
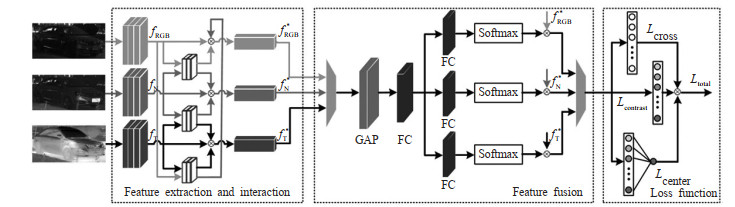
摘要: 针对可见光传感器弱光照条件下分辨率受限及单一模态表征不足导致的车辆再识别准确率低的问题,研究了基于特征动态交互和多模态自适应融合的车辆再识别方法。在网络结构方面,将SimAM模块嵌入到YOLOv9模型的骨干网络卷积层,在不引入额外参数的前提下,对不同模态特征间的空间与通道关系进行建模,提取可见光、近红外、远红外模态的初始特征。构建多模态特征交互模块,对3种模态进行特征精细提取并进行模态间信息的交互聚合,提取3种模态的增强特征。搭建多模态自适应特征融合网络,通过提取3种模态的全局向量和掩膜向量,动态自适应生成相应模态的权重系数,进而实现多模态的特征融合。针对样本类内差异大、类间差异小、及同一车辆在不同场景下显著变化的特点,构造交叉熵损失、对比损失和中心损失等多重损失函数,实现多模态的车辆再识别。为验证所提方法的有效性,在多模态数据集RGBN300和RGBNT100上开展实验验证,并与主流方法进行对比分析。针对RGBN300数据集,mAP提升了20.6%、29.0%、5.0%和3.5%;针对RGBNT100数据集,mAP提升了22.5%、12.0%、3.7%和3.0%,Rank-1、Rank-5和Rank-10达到了95.1%、96.7%和96.9%。实验结果表明:通过特征交互和多模态自适应融合,所提取的融合特征更具判别性,车辆再识别性能得到了有效提升。Abstract: The limited resolution of visible-light sensors under weak illumination conditions and the insufficient representational capacity of a single modality lead to low vehicle re-identification accuracy. To address this problem, a vehicle re-identification method based on dynamic feature interaction and adaptive multi-modal fusion is proposed. In terms of network architecture, the SimAM module is embedded into the convolutional layers of the YOLOv9 backbone network without introducing additional parameters, enabling the modeling of spatial and channel relationships within features and extracting initial representations from visible, near-infrared, and far-infrared modalities. A multi-modal feature interaction module is then constructed to perform refined feature extraction and cross-modal information exchange, thereby obtaining enhanced features for all three modalities. Furthermore, a multi-modal adaptive feature fusion network is designed, in which the weighting coefficients for each modality are adaptively generated based on global vectors and mask vectors, achieving effective feature fusion. To handle large intra-class variance, small inter-class differences, and significant appearance variations of the same vehicle across different scenarios, ajoint loss function combining cross-entropy loss, contrastive loss, and center loss is introduced. The proposed method is trained and validated on the publicly available datasets RGBN300 and RGBNT100. The results show that compared with existing methods, the mean average precision (mAP) and the recognition accuracy of Rank-1, Rank-5, and Rank-10 are improved to varying degrees. Among them, mAP is improved by 20.6%, 29.0%, 5.0%, and 3.5% on the RGBN300 dataset, and 22.5%, 12.0%, 3.7%, and 3.0% on the RGBNT100 dataset. Rank-1, Rank-5, and Rank-10 of the RGBNT100 dataset achieves 95.1%, 96.7%, and 96.9%. The experimental results show that feature interaction and adaptive multi-modal fusion lead to more discriminative features and excellent vehicle re-identification performance.
-
表 1 参数设置
Table 1. Parameters setting
参数 值 图像尺寸 256×256 批大小 16 Epochs 120 Learning rate 40-td epoch 3.5×10-5 Learning rate 80-td epoch 3.5×10-6 表 2 不同参数γ在数据集RGBNT100的评价结果
Table 2. Different parameter γ and the corresponding evaluation results on the RGBNT100 dataset
γ EmAP/% ERank - 1/% 0.000 1 73.9 77.6 0.001 76.1 80.2 0.01 74.8 76.9 0.1 74.9 77.8 1 74.2 77.0 表 3 不同车辆再识别算法的主干网络和超参数对比
Table 3. Comparisons of Backbone Networks and parameters of different vehicle Re-identification methods
表 4 不同车辆再识别算法的实验结果对比
Table 4. Comparisons of experimental results of different vehicle Re-identification methods
表 5 模态消融实验
Table 5. Ablation experiments of four groups
方法 RGBNT100 EmAP/% ERank - 1/% ERank - 5/% ERank - 10/% RGB 52.9 73.5 77.4 80.8 RGB+NIR 65.6 86.4 88.6 90.2 RGB+TIR 74.1 91.0 92.8 94.8 RGB+NIR+TIR 77.8 95.1 96.7 96.9 表 6 损失函数消融实验
Table 6. Ablation experiments of different loss functions
方法 RGBNT100 EmAP/% ERank - 1/% ERank - 5/% ERank - 10/% Lcross 72.5 92.0 94.7 95.6 Lcontrast 73.6 88.9 91.1 92.0 Lcenter 3.8 4.2 7.2 8.9 Lcross + Lcontrast 74.9 94.9 95.8 96.1 Lcross + Lcenter 75.7 94.5 95.7 95.9 Lcontrast + Lcenter 76.3 91.8 93.4 94.3 Lcross + Lcontrast + Lcenter 77.8 95.1 96.7 96.9 表 7 对比消融实验的8组实验配置
Table 7. Experiment configurations of the eight groups in the ablation experiment
表 8 8组消融实验的结果
Table 8. Results of 8 ablation experiments
组 EmAP/% ERank - 1/% ERank - 5/% ERank - 10/% 1 67.7 87.9 89.2 91.4 2 68.5 89.6 90.4 93.3 3 71.8 90.5 92.1 93.9 4 73.2 91.8 93.5 94.7 5 71.2 90.3 91.8 93.1 6 72.9 91.7 92.6 94.2 7 74.6 93.2 94.5 95.1 8 77.8 95.1 96.7 96.9 -
[1] SUN W, HU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Adversarial style-irrelevant feature learning with refined soft pseudo labels for domain-adaptive vehicle re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25 (12): 20602-20615. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3480156 [2] 张逸凡, 聂琳真, 黄灏然, 等. 基于改进YOLOv5算法的道路交通参与者实时检测方法[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2024, 42 (1): 115-123. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2024.01.013ZHANG Y F, NIE L Z, HUANG H R, et al. A method of real-time detection for road traffic participants based on an improved YOLOv5 algorithm[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2024, 42(1): 115-123(. in Chinese doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2024.01.013 [3] 张念, 张亮. 基于深度学习的公路货车车型识别[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(1): 267-279.ZHANG N, ZHANG L. Type recognition of highway trucks based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(1): 267-279(. in Chinese [4] 梁华刚, 黄伟浩, 薄颖, 等. 基于多特征融合的隧道场景车辆再识别[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(8): 280-291.LIANG H G, HUANG W H, BO Y, et al. Multi-feature-fusion-based vehicle re-identification for tunnel scenes[J]. China Journal of Highway Transportation, 2023, 36(8): 280-291. [5] 徐岩, 郭晓燕, 荣磊磊. 无监督学习的车辆重识别方法研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(5): 1017-1037.XU Y, GUO X Y, RONG L L. Review of research on vehicle re-identification methods with unsupervised learning[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2023, 17 (5): 1017-1037(. in Chinese [6] KHORRAMSHAHI P, SHENOY V, CHELLAPPA R. Robust and scalable vehicle re-identification via self-supervision[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. [7] ZHANG F, ZHANG L, ZHANG H, et al. Image-to-image domain adaptation for vehicle re-identification[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(26): 40559-40584. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-14839-7 [8] SHEN F, XIE Y, ZHU J, et al. Git: graph interactive transformer for vehicle re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32(1): 1039-1051. [9] HE Z, ZHAO H, WANG J, et al. Multi-level progressive learning for unsupervised vehicle re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 72(4): 4357-4371. [10] 马浩为, 张笛, 李玉立, 等. 基于改进YOLOv5的雾霾环境下船舶红外图像检测算法[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2023, 41 (1): 95-104. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2023.01.010MA H W, ZHANG D, LI Y L, et al. A ship detection algorithm for infrared images under hazy environment based on an improved YOLOv5 algorithm[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2023, 41(1): 95-104(. in Chinese doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2023.01.010 [11] ZAKRIA, DENG J H, KHOKHAR M S, et al. Trends in vehicle re-identification past, present, and future: a comprehensive review[J]. Mathematics. 2021, 24(9): 3162. [12] 蓝章礼, 王超, 杨晴晴, 等. 基于多粒度特征分割的车辆重识别算法[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41 (9): 7-15.LAN Z L, WANG C, YANG Q Q, et al. Vehicle re-identification algorithm based on multi-granularity feature segmentation[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science), 2022, 41(9): 7-15(. in Chinese [13] 刘凯, 李浥东, 林伟鹏. 车辆再识别技术综述[J]. 智能科学与技术学报, 2020, 2(1): 11-25.LIU K, LI Y D, LIN W P. A survey on vehicle re-identification[J]. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2020, 2(1): 11-25(. in Chinese [14] WANG S, WANG Q, MIN W, et al. Trade-off background joint learning for unsupervised vehicle re-identification[J]. The Visual Computer, 2023, 39(8): 3823-3835. doi: 10.1007/s00371-023-03034-2 [15] ZHAO Q Q, ZHAN S M, CHENG R, et al. A benchmark for vehicle re-identification in mixed visible and infrared domains[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024, 31: 726-730. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2024.3370492 [16] LI H, LI C, ZHU X, et al. Multi-spectral vehicle re-Identification: A challenge[C]. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, America: AAAI, 2020. [17] ZHENG A H, ZHU X P, Ma Z, et al. Cross-directional consistency network with adaptive layer normalization for multi-spectral vehicle re-identification and a high-quality benchmark[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 100(3): 101901. [18] HE Q L, LU Z F, WANG Z H, et al. Graph-based progressive fusion network for multi-modality vehicle re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(11): 12431-12447. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3285758 [19] YANG L, ZHANG R Y, LI L, et al. SimAM: A simple, parameter-Free attention module for convolutional neural networks[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2021. [20] 黄文心, 钟忺, 张军, 等. 基于组件超分辨率的多分辨率车辆重识别方法[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2022, 44(11): 96-104.HUANG W X, ZHONG X, ZHANG J, et al. Multi-resolution vehicle re-identification method based on component super-resolution[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2022, 44(11): 96-104(. in Chinese [21] 廖琳蔚, 杨卓倩, 杨鸿泰, 等. 基于多粒度级联森林的高排放重型柴油车辆的识别方法[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2024, 22(4): 166-181.LIAO L W, YANG Z Q, YANG H T, et al. Identification of high-emission heavy-duty diesel vehicles based on multigrained cascade forest[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2024, 22(4): 166-181(. in Chinese [22] 苏育挺, 陆荣烜, 张为. 基于注意力和自适应权重的车辆重识别算法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2023, 57(4): 712-718.SU Y T, LU R H, ZHANG W. Vehicle re-identification algorithm based on attention mechanism andadaptive weight[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science), 2023, 57(4): 712-718(. in Chinese [23] 孙伟, 赵宇煌, 张小瑞, 等. 基于弱监督注意力和知识共享的车辆重识别[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2023, 37(9): 179-189.SUN W, ZHAO Y H, ZHANG X R, et al. Weakly supervised attention and knowledge sharing for vehicle re-identification[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2023, 37(9): 179-189. [24] HE S, LUO H, WANG P, et al. TransReID: transformer-based object re-identification[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference ComputerVision, Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. [25] GUO J, ZHANG X, LIU Z, et al. Generative and attentive fusion for multi-spectral vehicle re-identification[C]. 7th International Conference Intelligent Computer Signal Processing, Xi'an China: IEEE, 2022. -





 下载:
下载: