Coordinated Optimization Method for Feeder Container Ship Route Planning and Stowage Based on DQN Algorithm
-
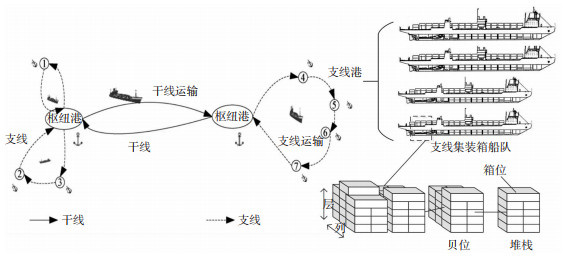
摘要: 针对支线集装箱船运输中喂给港数和靠泊条件不一,以及集装箱船队船型多样的特点,考虑航线规划与配载环节在实际运输过程中的紧密联系,研究支线集装箱船航线规划与配载协同优化方法。采用两阶段分层方法研究航线规划与集装箱配载问题,设置多个港口、不同船型及其贝位和堆栈组合、不同尺寸集装箱的集合,并确定其间基本关系,实现两阶段优化过程的完整性和连续性。第一阶段以航线总运营成本最小为目标建立船舶航线规划模型,第二阶段从主贝计划角度出发进行配载优化,确认集装箱与堆栈的对应关系,以船舶混装堆栈数最小为目标建立船舶配载模型,保证船舶稳性在航线任意时段均满足要求,并减少堆栈混装数量,提高到港作业效率。为实现模型高效求解,基于深度强化学习的Deep Q-learning Network(DQN)算法架构,设计了航线规划与配载决策对应的马尔可夫过程,结合问题自身特征分别完成强化学习智能体状态空间、动作空间以及奖励函数设计,构建了两阶段分层求解的DQN算法。实验结果表明:随着船舶数量和船舶装载率的增加,模型精确求解的时间大幅增加,部分算例无法在600 s内完成求解,而DQN算法可实现快速求解;与模型及粒子群优化(Particle Swarm Optimization,PSO)算法相比,DQN算法可高效求解不同规模下的算例,大规模算例求解最大耗时31.40 s,平均耗时30 s以内,求解效率较好;进一步计算表明,不同喂给港数量下PSO算法在求解时间上的平均标准差为11.20,而DQN算法平均标准差仅为1.74,鲁棒性更好。总体来看,DQN算法在求解时间上随问题规模变化而产生的波动较小,具有更加稳定的求解性能,可实现高效寻优。Abstract: Given the unique features of feeder container shipping, including varying feeder port numbers and inconsistent berthing conditions, as well as the divers' types of container fleets, this research investigates the coordinated optimization for route planning and stowage in feeder container shipping considering their close connection in the actual transportation process. A two-stage hierarchical method is employed to study the route planning and container stowage problems. Multiple ports, different ship types with their respective bays and stack combinations, and containers of various sizes are included in the study. The fundamental relationships among these elements are established to achieve integrity and continuity of the two-stage optimization process. The first stage involves establishing a ship route planning model with the objective of minimizing the total operational cost. The second stage focuses on optimizing the stowage from the perspective of primary bay planning. The correspondence between containers and stacks is determined, and a ship stowage model is developed with the objective of minimizing the number of mixed container stacks. The stowage model ensures that the ship's stability meets the requirements throughout the route, while reducing the number of mixed stacks to improve port operation efficiency. To efficiently solve the proposed models, a Markov process corresponding to route planning and stowage decision-making is designed based on the Deep Q-learning Network (DQN) algorithm from deep reinforcement learning. The intelligent agent's state space, action space, and reward function are designed based on the problem's characteristics to construct the two-stage hierarchical DQN algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate that as the number of ships and the ship loading rate increase, the time required for accurate model solution significantly rises. Some cases cannot be solved within 600 seconds, while the DQN algorithm achieves rapid solutions in all examples. Compared with traditional models and the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm, the DQN algorithm efficiently solves cases of different scales. The maximum solving time for large-scale cases is 31.40 s, with an average time of less than 30 s, indicating good solution efficiency. Further calculations indicate that under different feeder port numbers, the average standard deviation of solving time for the DQN algorithm is only 1.74, showing better robustness compared to the average standard deviation of 11.20 for the PSO algorithm. Overall, the DQN algorithm exhibits less fluctuation in solving time with changing problem scales, showcasing stable solving performance and efficient optimization capabilities.
-
表 1 船舶主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the ship
编号 贝位 列 层 堆栈 单列载重/t 总容量/TEU 1 4 4 3 16 45 96 2 6 4 4 24 60 192 3 8 4 4 32 60 256 4 8 6 5 48 75 480 表 2 不同港口数目
Table 2. Different number of ports
编号 港口数目 喂给港数 P7 7 6 P11 11 10 P15 15 14 表 3 不同装载率
Table 3. Differentloading ratio
编号 装载率/% C45 45 C65 65 C85 85 表 4 港口数P7求解结果
Table 4. Results for case P7
算例 Gurobi PSO DQN f1 f2 T f1 f2 T f1 f2 T $S_2 P_7 C_{45}$ 222.91 19 0.43 222.91 21 4.63 222.91 21 5.82 $S_2 P_7 C_{65}$ 222.91 25 0.54 222.91 26 6.10 222.91 25 5.78 $S_2 P_7 C_{85}$ 268.73 18 0.50 282.54 20 6.96 268.73 18 5.51 $S_3 P_7 C_{45}$ 268.73 18 0.56 268.73 18 7.26 268.73 18 5.30 $S_3 P_7 C_{65}$ 268.73 18 0.59 268.73 18 5.14 268.73 18 5.38 $S_3 P_7 C_{85}$ 328.36 26 0.67 328.36 26 13.64 328.36 27 5.62 $S_4 P_7 C_{45}$ 222.91 52 0.79 268.73 57 14.99 222.91 55 6.28 $S_4 P_7 C_{65}$ 282.54 76 0.64 282.54 77 28.64 282.54 76 7.06 $S_4 P_7 C_{85}$ 341.14 87 0.94 341.14 89 26.70 341.14 87 8.21 表 5 港口数P11求解结果
Table 5. Results for case P11
算例 Gurobi PSO DQN f1 f2 T f1 f2 T f1 f2 T $S_2 P_{11} C_{45}$ 309.48 22 1.82 355.25 25 8.87 344.04 22 21.7 $S_2 P_{11} C_{65}$ 309.48 34 2.58 355.25 34 10.41 344.04 41 22.98 $S_2 P_{11} C_{85}$ 355.25 40 3.77 383.6 42 7.21 378.63 40 23.02 $S_3 P_{11} C_{45}$ 309.48 37 6.29 355.25 38 11.08 346.54 28 24.06 $S_3 P_{11} C_{65}$ 355.25 52 5.94 355.25 52 14.98 387.68 49 25.65 $S_3 P_{11} C_{85}$ 411.68 67 18.34 440.09 69 18.13 444.49 66 25.35 $S_4 P_{11} C_{45}$ 309.48 54 11.74 355.25 59 17.32 344.04 61 26.84 $S_4 P_{11} C_{65}$ 369.07 80 11.9 378.63 80 33.64 369.07 80 26.77 $S_4 P_{11} C_{85}$ 425.51 105 21.32 443.25 100 34.93 446.79 100 28.31 表 6 港口数P15求解结果
Table 6. Results for case P15
算例 Gurobi PSO DQN f1 f2 T f1 f2 T f1 f2 T $S_2 P_{15} C_{45}$ 349.98 27 116.83 389.98 28 14.42 368.45 27 24.55 $S_2 P_{15} C_{65}$ 349.98 31 118.02 405.07 38 16.66 374.83 36 25.44 $S_2 P_{15} C_{85}$ 389.98 42 201.76 444.97 48 13.75 435.57 46 25.69 $S_3 P_{15} C_{45}$ 349.98 38 241.73 444.05 44 19.51 426.83 39 26.54 $S_3 P_{15} C_{65}$ - - 600 421.88 55 23.76 418.35 54 28.96 $S_3 P_{15} C_{85}$ - - 600 447.5 72 28.90 440.71 69 27.99 $S_2 P_{15} C_{45}$ - - 600 449.01 65 26.51 430.67 59 29.54 $S_4 P_{15} C_{65}$ - - 600 390.63 83 54.58 372.13 80 30.33 $S_4 P_{15} C_{85}$ - - 600 457.88 109 55.59 424.43 104 31.40 -
[1] OVSTEBO B, HVATTUM L, FAGERHOLT K. Routing and scheduling of RoRo ships with stowage constraints[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2011, 19 (6): 1225-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2011.02.001 [2] 陈忱. 最优航线调度和集装箱船舶配载计划的决策支持系统[D]. 天津: 天津理工大学, 2012.CHEN Y. Decision support system for optimal route scheduling and container ship stowage planning[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese) [3] MOURA A, OLIVEIRA J, PIMENTEL C. A mathematical model for the container stowage and ship routing problem[J]. Journal of Mathematical Modelling and Algorithms in Operations Research, 2013, 12(3): 217-231. doi: 10.1007/s10852-012-9207-3 [4] MOURA A, OLIVEIRA J. Exact solutions to the short sea shipping distribution problem[C]. IO 2013-XVI Congress of APDIO, Braganca, Portugal: Operational Research, 2015. [5] JI M, KONG L, GUAN Y. Integrated optimization of feeder routing and stowage planning for containerships[J]. Soft Computing, 2021, 25(1): 4465-4487. [6] CHRISTIANSEN M, NYGREEN B. A method for solving ship routing problems with inventory constraints[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 1998, 81(6): 357-378. [7] AGARWAL R, ERGUN O. Ship scheduling and network design for cargo routing in linear shipping[J]. Transportation Science, 2008, 42(2): 175-196. doi: 10.1287/trsc.1070.0205 [8] KIM J, SON H, YANG W, et al. Liner ship routing with speed and fleet size optimization[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering, 2019, 23(3): 1341-1350. [9] CHARALAMBOPOULOS N, NEARCHOU C. Ship routing using genetic algorithms[J]. Operations Research Forum, 2021, 2(45): 1-26. [10] 计明军, 陈哲, 王清斌. 集装箱船舶支线运输航线优化算法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2011, 11(4): 68-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC201104010.htmJI M J, CHEN Z, WANG Q B. Optimization algorithm of branch transportation route for container ship[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation, 2011, 11(4): 68-75. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC201104010.htm [11] 郑红星, 李珊珊, 司羽. 内支线配船与船舶调度优化[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 38(2): 109-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT201902016.htmZHENG H X, LI S S, SI Y. Internal feeder ship allocation and ship dispatching optimization[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science), 2019, 38(2): 109-116. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT201902016.htm [12] AMBROSINO D, SCIOMACHEN A, TANFANI E. Stowing a containership: the master bay plan problem[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy & Practice, 2004, 38(2): 81-99. [13] AMBROSINO D, PAOLUCCI M, SCIOMACHEN, A. Experimental evaluation of mixed integer programming models for the multi-port master bay plan problem[J]. Flexible Services & Manufacturing Journal, 2015, 27(2-3): 263-284. [14] MARIA M, MARCELLO S, GREGORIO S. The terminal-oriented ship stowage planning problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2014, 239(1): 256-265. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2014.05.030 [15] 张华胜. 基于深度强化学习的自动化码头跨运车集成调度研究[D]. 上海: 上海海事大学, 2022.ZHANG H S. Research on integrated scheduling of shuttle carriers in automated terminals based on deep reinforcement[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Maritime University, 2022. (in Chinese) [16] 段振堂. 基于深度强化学习的集装箱堆叠优化算法研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2023.DUAN Z T. Research on container stacking optimization algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2023. (in Chinese) [17] 李俊. 内河集装箱班轮航线配载决策研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019.LI J. Route stowage planning decision for inland container liner shipping[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2019. (in Chinese) [18] HAN B A, YANG J J. Research on adaptive job shop scheduling problems based on dueling double DQN[J]. IEEE Access, 2020(8): 186474-186495. [19] GU B, SUNG Y. Enhanced DQN framework for selecting actions and updating replay memory considering massive non-executable actions[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(23): 1-15. [20] 尹星, 张煜, 郑倩倩, 等. 基于深度强化学习的自动化集装箱码头集成调度方法[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2022, 40(6): 81-91. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2022.06.009?viewType=HTMLYIN X, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Q Q, etal. A study of integrated scheduling of automated container terminal based on DDQN[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2022, 40(6): 81-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2022.06.009?viewType=HTML [21] YANG Y, LI J T, PENG L L. Multi-robot path planning based on a deep reinforcement learning DQN algorithm[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2020, 5(3): 117-183. -





 下载:
下载: