A Programming Model for the Flexible Multi-depot Heterogeneous Dial-a-ride Problems
-
摘要: 为解决1种新的叫车接送问题(DARP)——灵活多车场多类型的叫车接送问题(MDHDARP-FD),建立以总行驶成本最小为目标的混合整数非线性规划数学模型。由于模型非常复杂,难以直接求解,对模型进行约束线性化、变量聚合和添加有效不等式等处理。在约束线性化过程中,非线性约束被重写为等价的线性约束;在变量聚合过程中,将具有相同性质的决策变量进行聚合,以减少变量数量;还引入了一些有效不等式来强化模型。从而获得1个解空间较小易于求解的新线性规划模型,并结合不同类型的车辆和乘客需求进行叫车接送问题的仿真测试。算例结果表明,相比于传统叫车接送问题,该模型能在满足复杂约束的基础上,得到1组实现乘客接送需求的最优车辆路线,并且能有效降低总行驶成本、车辆行驶时间和求解时间,总行驶成本在不同类型的DARP上可平均降低1.51%~6.69%,证实了叫车接送问题的总行驶成本可以随着灵活车场的引入而减少。Abstract: A mathematical model of mixed-integer non-linear programming is firstly constructed to solve a new dial-a-ride problem(DARP), the multi-depot heterogeneous dial-a-ride problem with flexible depots(MDHDARP-FD), as well as minimize the total driving cost.Due to the complexity of the proposed model, some strategies of linearizing constraints, aggregating variables, and strengthening inequalities are performed to reformulate the non-linear model.During linearizing constraints, non-linear constraints are rewritten as equivalent linear constraints.Aggregating variables, decision variables with the same properties, are aggregated to reduce the number of variables, with strengthened inequalities and valid inequalities introduced to strengthen the model.As a result, a new linear programming model with a small solution space is obtained and can be tractable.Then the dial-a-ride problem is simulated by combining different vehicles and passengers'demands.Simulation results show that compared with the traditional dial-a-ride problems, the model can obtain a group of optimal vehicle routes respecting the complex constraints and reduce the total driving cost, vehicle driving time, and solution time.The total driving cost can be reduced by 1.51%to 6.69%for different DARPs on an average, verifying that the total driving cost of dial-a-ride problems can be reduced with the introduced flexible depots.
-
表 1 算例Ea4-16的乘客需求信息
Table 1. Passengers'demand information of Example Ea4-16
序号 横坐标 纵坐标 服务时间/min 最大乘车时间/ min 位置需求 时间窗下界/min 时间窗上界/min 常规座位(员工座位) 常规座位(病人座位) 担架位 轮椅位 1 6.267 0.981 3 30 0 0 0 1 0 1 440 2 —4.718 6.925 3 30 0 1 0 0 0 1 440 3 3.254 7.621 3 30 0 1 0 0 0 1 440 4 9.654 2.799 3 30 0 0 1 0 0 1 440 5 8.575 2.701 3 30 0 1 0 0 0 1 440 6 —9.732 —8.314 3 30 0 1 0 0 0 1 440 7 9.937 4.969 3 30 0 0 0 1 0 1 440 8 —4.604 6.053 3 30 0 0 0 1 0 1 440 9 —5.029 5.070 3 30 0 1 0 0 53 68 10 —9.264 —7.979 3 30 0 1 0 0 105 120 11 8.738 —9.966 3 30 0 1 0 0 74 89 12 —3.420 7.617 3 30 0 0 1 0 3 18 13 —5.865 —4.571 3 30 1 1 0 0 172 187 14 6.300 5.322 3 30 0 0 0 1 61 76 15 —2.219 —7.605 3 30 0 1 0 0 179 194 16 —1.654 —7.838 3 30 0 1 0 0 154 169 17 —1.548 —4.124 3 0 0 0 0 —1 138 153 18 —4.818 6.259 3 0 0 —1 0 0 125 140 19 —7.389 0.376 3 0 0 —1 0 0 95 110 20 6.070 —0.549 3 0 0 0 —1 0 195 210 21 —1.663 6.171 3 0 0 —1 0 0 103 118 22 —0.665 —1.272 3 0 0 —1 0 0 103 118 23 —5.005 0.918 3 0 0 0 0 —1 142 157 24 6.200 —7.679 3 0 0 0 0 —1 157 172 25 5.575 —7.408 3 0 0 —1 0 0 0 1 440 26 —7.754 3.535 3 0 0 —1 0 0 0 1 440 27 2.111 1.439 3 0 0 —1 0 0 0 1 440 28 1.706 —1.733 3 0 0 0 —1 0 0 1 440 29 —1.796 9.104 3 0 —1 —1 0 0 0 1 440 30 —5.500 2.353 3 0 0 0 0 —1 0 1 440 31 7.323 —7.149 3 0 0 —1 0 0 0 1 440 32 —6.413 0.367 3 0 0 —1 0 0 0 1 440 表 2 算例Ea4-16的模型求解结果
Table 2. Model solution results of Example Ea4-16
约束条件总数 变量总数 整数变量 运行时间/s 总行驶成本 20 385 3 852 3 780 1 661.44 257.00 表 3 算例Ea4-16的最优接送路线
Table 3. Optimal route of Example Ea4-16
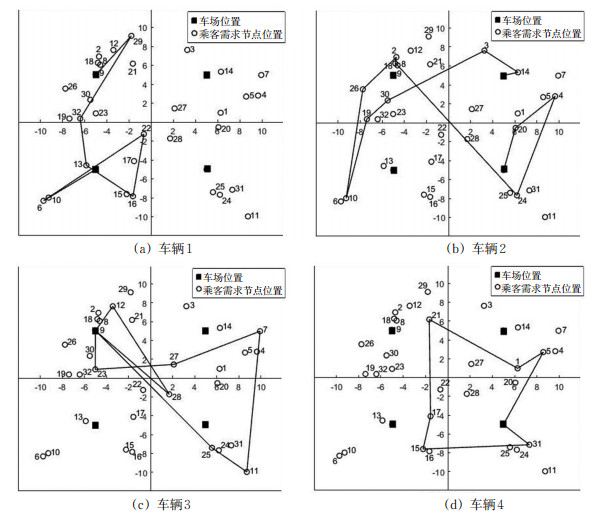
车辆序号 出发车场坐标 最优接送路线 返回车场坐标 1 [-5,-5] -6-22-16-13-32-29- [-5,5] 2 [5,5] -14-3-30-19-10-26-2-18-8-24-4-20- [5,-5] 3 [-5,5] -12-28-9-25-11-7-27-23- [-5,5] 4 [5,-5] -5-1-21-17-15-31- [5,-5] 表 4 系列算例求解结果及比较
Table 4. Comparison results of examples
Dataset Instance MDHDARP-FD CPU/s MD-H-DARP G1/% H-DARP G2/% 2-index-DARP G3/% DARP G4/% Ua2-16 284.18 1.38 284.18 0.00 294.25 3.42 300.17 5.33 294.25 3.42 Ua2-20 333.57 8.67 343.43 2.87 344.83 3.27 345.74 3.52 344.83 3.27 Ua2-24 426.75 28.14 427.17 0.10 431.12 1.01 448.07 4.76 431.12 1.01 Ua3-18 279.05 31.89 289.67 3.67 300.48 7.13 316.78 11.91 300.48 7.13 Dataset U Ua3-24 344.60 1 062.13 348.30 1.06 344.83 0.07 346.97 0.68 344.83 0.07 Ua3-30 468.78 45 053 469.16 0.08 494.85 5.27 501.68 6.56 472.17 0.72 Ua4-16 252.03 3 231.39 262.44 3.97 282.68 10.84 282.68 10.84 282.68 10.84 Ua4-24 348.26 78 368.40 355.72 2.10 375.02 7.14 386.38 9.87 359.52 3.13 AVG 342.15 15 973.13 347.51 1.54 358.51 4.56 366.06 6.69 353.734 3.28 Ea2-16 327.67 2.58 327.67 0.00 331.13 1.04 331.13 1.04 331.13 1.04 Ea2-20 335.76 8.62 345.59 2.84 347.03 3.25 347.89 3.49 347.03 3.25 Ea2-24 443.08 56.03 445.88 0.63 450.21 1.58 461.89 4.07 451.27 1.81 Ea3-18 279.05 41.66 289.67 3.67 300.63 7.18 316.78 11.91 300.63 7.18 Dataset E Ea3-24 344.67 1 039.07 348.61 1.13 344.91 0.07 347.05 0.69 345.04 0.11 Ea3-30 471.43 28 200.70 471.43 0.00 500.53 5.81 501.68 6.03 476.28 1.02 Ea4-16 257.00 1 661.44 262.44 2.07 285.99 10.14 288.7 10.98 286.07 10.16 Ea4-24 354.97 88 246.60 365.54 2.89 380.48 6.70 386.38 8.13 365.65 2.92 AVG 351.70 14 907.09 357.10 1.51 367.61 4.33 372.69 5.79 362.88 3.09 -
[1] DAGANZO C F, OUYANG Y. A general model of demand-responsive transportation services: From taxi to ridesharing to dial-a-ride[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2019(126): 213-224. http://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/transb/v126y2019icp213-224.html [2] CÉLIA P, CRAMA Y, PIRONET T. Recovery management for a dial-a-ride system with real-time disruptions[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 280(3): 953-969. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.08.006 [3] HO S C, SZETO W Y, KUO Y H, et al. A survey of dial-a-ride problems: Literature review and recent developments[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2018(111): 395-421. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191261517304484 [4] 孙博, 杨春风, 魏明, 等. 基于集对分析的随机需求接驳公交调度模型[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2018, 36(6): 130-134. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2018.06.017SUN Bo, YANG Chunfeng, WEI Ming, et al. A scheduling model of shuttle buses for stochastic demand passengers based on set pair analysis[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2018, 36(6): 130-134. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2018.06.017 [5] 孙继洋, 黄建玲, 陈艳艳, 等. 响应动态需求的灵活型公交路径优化调度模型[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(3): 269-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD202103009.htmSUN Jiyang, HUANG Jianling, CHEN Yanyan, et al. Flexible bus route optimal scheduling model in response to dynamic demand[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(3): 269-279. (in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD202103009.htm [6] PARRAGH S N, DOERNER K F, HARTL R F. Variable neighborhood search for the dial-a-ride problem[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2010, 37(6): 1129-1138. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030505480900241X [7] HÄME L. An adaptive insertion algorithm for the single-vehicle dial-a-ride problem with narrow time windows[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 209(1): 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2010.08.021 [8] PARRAGH S N, SCHMID V. Hybrid column generation and large neighborhood search for the dial-a-ride problem[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2013, 40(1): 490-497. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0305054812001694 [9] MUELAS S, LATORRE A, PEÑA J M. A distributed VNS algorithm for optimizing dial-a-ride problems in large-scale scenarios[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015(54): 110-130. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0968090X15000790 [10] RITZINGER U, PUCHINGER J, HARTL R F. Dynamic programming based metaheuristics for the dial-a-ride problem[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2016, 236(2): 341-358. doi: 10.1007/s10479-014-1605-7 [11] TRIPATHY T, NAGAVARAPU S C, AZIZIAN K, et al. Solving dial-a-ride problems using multiple ant colony system with fleet size minimisation[C]. 17th Annual UK Workshop on Computational Intelligence: Advances in Computational Intelligence Systems, Cardiff, UK: UKCI, 2017. [12] MASMOUDI M A, BRAEKERS K, MASMOUDI M, et al. A hybrid genetic algorithm for the heterogeneous dial-a-ride problem[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2017, 81(C): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2016.12.008 [13] CORDEAU J F. A branch-and-cut algorithm for the dial-a-ride problem[J]. Operations Research, 2006, 54(3): 573-586. doi: 10.1287/opre.1060.0283 [14] ROPKES, LAPORTEG, CORDEAUJ F. Models andbranch-andcut algorithms for pickup and delivery problems with time windows[J]. Networks: An International Journal, 2007, 49(4): 258-272. doi: 10.5555/1276833.1276836 [15] LIU M, LUO Z, LIM A. A branch-and-cut algorithm for a realistic dial-a-ride problem[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2015, 81(1): 267-288. [16] WONG K I, BELL M G H. Solution of the dial-a-ride problem with multi-dimensional capacity constraints[J]. International Transactions in Operational Research, 2006, 13(3): 195-208. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-3995.2006.00544.x [17] PARRAGH S N. Introducing heterogeneous users and vehicles into models and algorithms for the dial-a-ride problem[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2011, 19(5): 912-930. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2010.06.002 [18] PARRAGH S N, CORDEAU J F, DOERNER K F, et al. Models and algorithms for the heterogeneous dial-a-ride problem with driver-related constraints[J]. OR Spectrum, 2012, 34(3): 593-633. doi: 10.1007/s00291-010-0229-9 [19] BRAEKERS K, CARIS A, JANSSENS G K. Exact and meta-heuristic approach for a general heterogeneous dial-a-ride problem with multiple depots[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2014(67): 166-186. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191261514000800 [20] BRAEKERS K, KOVACS A A. A multi-period dial-a-ride problem with driver consistency[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2016(94): 355-377. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0191261515301570 [21] MOLENBRUCH Y, BRAEKERS K, AN C, et al. Multi-directional local search for a bi-objective dial-a-ride problem in patient transportation[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2017, 77(C): 58-71. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0305054816301861 [22] KEK A G H, CHEU R L, MENG Q, Distance-constrained capacitated vehicle routing problems with flexible assignment of start and end depots[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2008(47): 140-152. [23] MARKOV I, VARONE S, BIERLAIRE M. Integrating a heterogeneous fixed fleet and a flexible assignment of destination depots in the waste collection VRP with intermediate facilities[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2016(84): 256-273. -





 下载:
下载: